Where resources are available, consider the roles of other primary care team members – nurse counsellors and primary care coordinator.
*Please refer to BMI Control and Smoking Cessation Care Protocols for lists of programmes.
Care teams may use
the relevant Lifestyle Prescription to help patients understand practical steps they can take to manage hypertension. A
copy may be printed for the patient's use.
Pharmacotherapy
a. Where pharmacotherapy is warranted, most patients would benefit from starting with a low dose. Overall, the choice of antihypertensive depends on several considerations, outlined in table 4 below. (Avoid initiating beta blockers (BBs) as first-line monotherapy for BP control unless BB use is expected to have favourable effect on patient comorbidities. BBs may be beneficial for patients who also require heart rate reduction, or have cardiac comorbidities such as stable ischaemic heart disease, chronic heart failure, or atrial fibrillation).
Table 4: Considerations for choosing a first-line antihypertensive class
.png) Source: Agency for Care Effectiveness (ACE).
Hypertension – tailoring the management plan to optimise blood pressure control. ACE Clinical Guidelines (ACG), Ministry of Health, Singapore. 2023.
Source: Agency for Care Effectiveness (ACE).
Hypertension – tailoring the management plan to optimise blood pressure control. ACE Clinical Guidelines (ACG), Ministry of Health, Singapore. 2023.
b. Starting with dual therapy may be appropriate if a greater reduction in BP is required to reach targets, such as for patients with SBP/DBP ≥20/10 mmHg above target, those with Grade 2 hypertension or higher (clinic BP ≥160/100 mmHg), or those with comorbidities such as DM or CKD who may require more intensive treatment.
The benefits and harms of various combinations are highlighted in Figure 1 and Table 5 below.
Figure 1: Possible Combinations for Dual Therapy to Treat Hypertension
.PNG) Table 5: Drug Combinations to Consider Avoiding
Table 5: Drug Combinations to Consider Avoiding
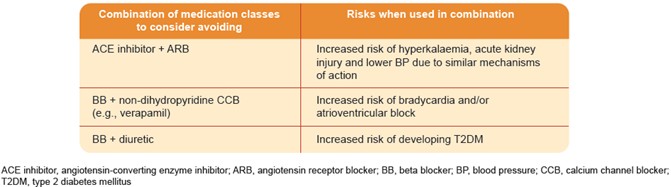
Source: Agency for Care Effectiveness (ACE).
Hypertension – tailoring the management plan to optimise blood pressure control. ACE Clinical Guidelines (ACG), Ministry of Health, Singapore. 2023.
Table 6: Recommended Care Components
|
Recommended Care Components |
Minimum Frequency* |
Remarks |
|
Blood Pressure Measurement |
Twice a year | |
|
Weight and Body Mass Index (BMI) Assessment |
Twice a year |
Keep <23 kg/m2 (For Non-Asian population, keep BMI <25 kg/m2). |
Kidney Assessment -
Serum Creatinine and/or estimated Glomerular Filtration Rate (eGFR),
and
-
Urine Albumin-Creatinine Ratio (uACR) or Protein-Creatinine Ratio (uPCR)
|
Annually |
If patient also has diabetes mellitus (DM), Angiotensin Converting Enzyme (ACE) inhibitor or Angiotensin Receptor Blocker (ARB) are preferred antihypertensives to slow progression of diabetic nephropathy.
Annual screening of: -
Serum Cr and/or eGFR and
-
uACR in all patients, or uPCR if significant levels of proteinuria
|
|
Smoking Assessment |
Annually for smokers; Once-off for non-smokers, unless there is a change in smoking habit |
Assessment on smoking habits (estimated sticks/day; zero for non- or ex-smoker) and provide smoking cessation counselling where applicable. |
|
Lipid Profile |
At baseline |
All patients should be stratified for their risk of developing future coronary events.5
Targets of treatment should be personalised by levels of risk.
Please refer to
Care Protocol for Lipid Disorders. |
|
Cardiac Assessment |
At diagnosis before initiating medications |
Includes baseline ECG.
|
*More frequently if clinically indicated.
Considerations for Specialist Referral3
|
Specialists can be consulted for advice, referral and collaborative care at any point, particularly for |
Patients with indications for emergency or urgent treatment, e.g., malignant hypertension, hypertensive cardiac failure or other impending complications.
Patients with difficult-to-manage hypertension, e.g., unusually labile BP.
Patients with hypertension with no or incomplete response to multiple medication regimes (three or more i.e. resistant hypertension).
Patients with suspected secondary hypertension, e.g. hypertension with hypokalaemia.
Hypertension in certain patient populations, e.g., pregnant women, young children, patients aged less than 30 years.
Patients with acute or recent cardiovascular complications from hypertension.
|
GPs may use the
CHAS Medical Referral Form to make subsidised SOC referrals and the GPFirst Referral Form for Emergency Department referrals. These can be found on Healthier SG-compatible GP CMS and on the PCDS web-portal.

